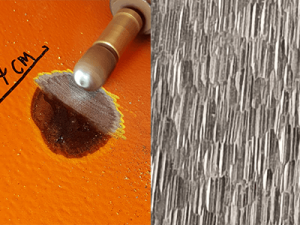
Heat damage
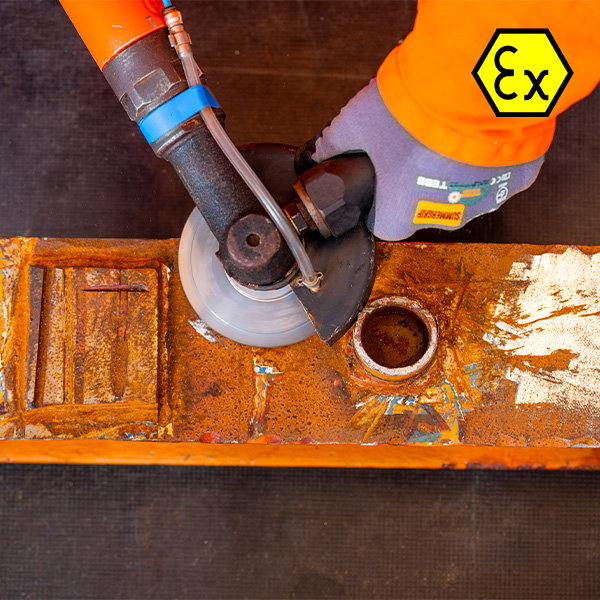
Conventional grinding discs/tools have many disadvantages, and one of the disadvantages is that they create hot sparks.
Heat damage from hot sparks
Conventional grinding discs/tools have many disadvantages, and one of the disadvantages is that they create hot sparks.
High rotational speeds and heat damage can create dangerous situations for the operator and damage to the substrate in paint.
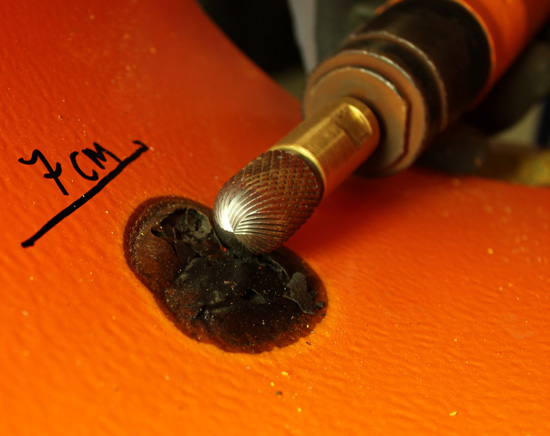
Temperature measurements on the substrate in the grinding areas have been found to be in the range of 500-1000°C
It is important to remember that the friction generated during a localized repair considerably raises the substrate temperature around the contact point and the immediate vicinity. Not to mention the flying sparks that land on the adjacent sound coating. The risk from sparks can, of course, be mitigated with proper masking. Using water (if allowed) during grinding could help dissipate some of the heat generated. However, it does come with a potential problem of flash rusting↵ of the prepared area.
Read more about Spot Repair Maintenance here:
Spot Repair Maintenance – Do conventional grinding discs hurt more than they heal?
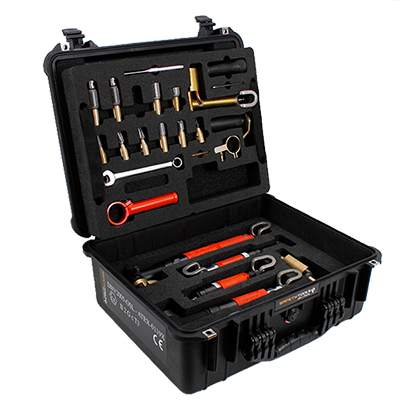
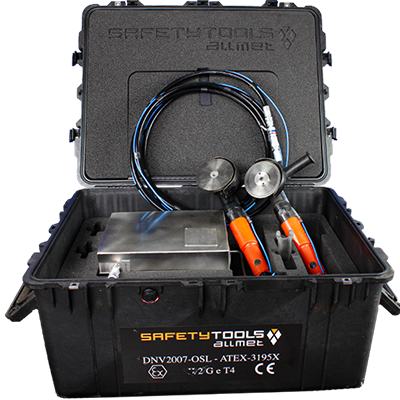
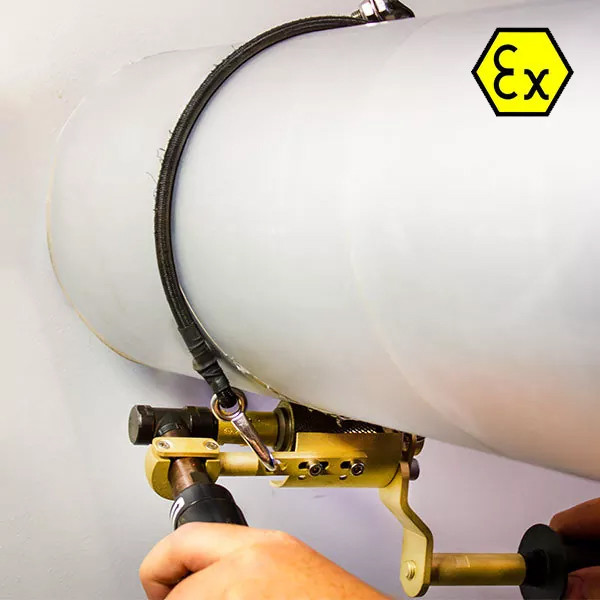
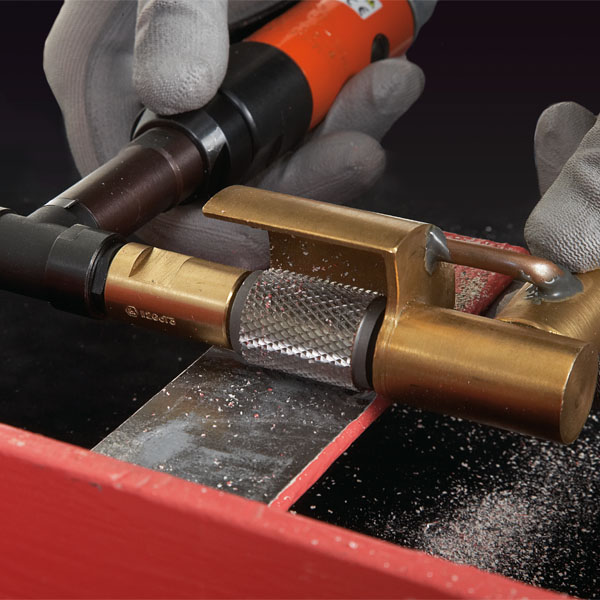
Mechanical pre-treatment tool that does NOT create heat damage
Safety Tools Allmet files and discs are made of solid tungsten carbide. The teeth’ hardness and design increase the lifetime of files and discs significantly. The fragments produced after grinding with Safety Tools Allmet are easy to clean, large, and blunt. This offers many safety and operational benefits compared to conventional tools.
Ex-certified cold work surface preparation tools from Safety Tools Allmet will give a good clean surface with a profile meeting the SSPC-SP11 Surface Preparation Standard requirements. This standard is suitable where a roughened, clean, bare metal surface free of all visible oil, grease, dirt, rust, coating, oxides, mill scale, corrosion products, and other foreign matter is required but where abrasive blasting is not feasible or permissible. Lastly, the peaks and valleys on the prepared surface need to form a continuous pattern with no smooth, unprofiled areas.